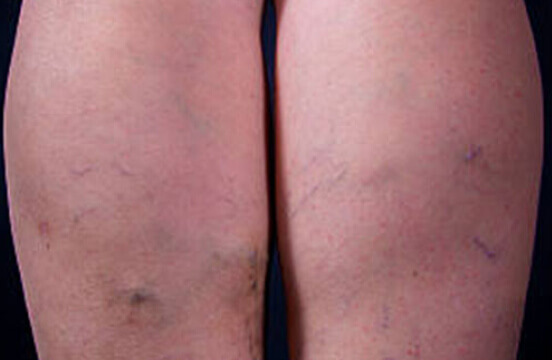
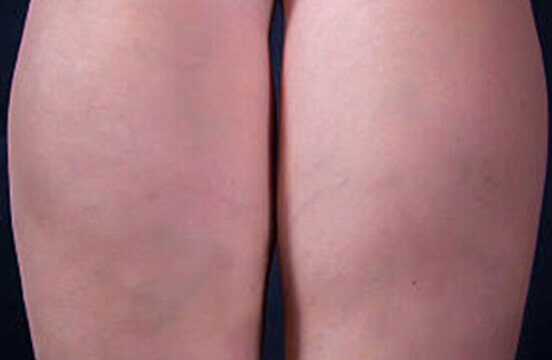
Lymphedema and Vein Care: Find a Vein Specialist Near You
Taking care of your veins should never be an afterthought, especially when a condition like Lymphedema is an ever-looming possibility. Lymphedema not only triggers uncomfortable swelling in extremities due to an impaired lymphatic system but also significantly increases the risk for serious vein-related conditions.
Led by Michigan vein specialist, Dr. Hamman Zmily, the team at Suburban Vein Center wants to help you better understand Lymphedema, the essential role of proper vein care in managing it, and most importantly, how visiting our top-tier vein specialist at one of the Michigan locations near you can make all the difference. Let us help you take charge of your health by choosing to be proactive today!
Understanding Lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphatic edema, is a chronic vein condition that often goes undiagnosed or misunderstood, yet it can have a significant impact on a person’s health and quality of life.
Think of your body’s lymphatic system as a network of roadways. These roadways carry a fluid made of a mixture of intestinal fluids (chyle) and white blood cells, called lymph. These roadways parallel your veins and arteries, working to remove waste and excess fluid from your tissues. This intricate system acts as a crucial component in maintaining healthy circulation.
However, various factors can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to lymphedema. In simple terms, lymphedema occurs when there’s an obstruction or damage to the lymphatic vessels or nodes, impeding the flow of lymph and causing it to accumulate in the affected area. This accumulation results in swelling, typically in the arms or legs but it can also occur in other parts of the body.
Causes of Lymphedema
The causes of lymphedema can be categorized into primary and secondary.
- Primary lymphedema is often inherited and presents itself at birth, puberty, or later in life.
- On the other hand, secondary lymphedema arises as a result of external factors.
Primary Lymphedema Causes
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited gene mutations affect the development or function of the lymphatic system.
- Milroy’s Disease (Congenital Lymphedema): A hereditary condition present at birth that leads to impaired lymphatic drainage.
- Meige’s Disease (Lymphedema Praecox): Occurs around puberty or early adulthood due to abnormalities in the lymphatic system.
- Late-Onset Lymphedema (Lymphedema Tarda): Develops after the age of 35 and may have a genetic basis.
Secondary Lymphedema Causes
- Cancer treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, or lymph node removal for cancer can damage lymph nodes and vessels, leading to secondary lymphedema.
- Infections: Filariasis, a parasitic infection transmitted through mosquito bites, is a common cause of secondary lymphedema in tropical regions. Certain parasitic infections other than filariasis can also cause lymphatic damage and secondary lymphatic edema.
- Injury or Trauma: Accidents, burns, or other trauma that damages the lymphatic system can cause secondary lymphedema.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Impaired blood flow in the veins can lead to fluid buildup and secondary lymphedema.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put pressure on the lymphatic system and hinder fluid drainage.
- Inflammatory conditions: Conditions like cellulitis, rheumatoid arthritis, or dermatitis can cause inflammation and damage to lymphatic vessels.
- Surgery: Any surgery that involves lymph node removal or disrupts the lymphatic system may lead to secondary lymphatic edema.
Signs and Symptoms of Lymphedema
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lymphedema is essential for timely intervention and management. While lymphatic edema primarily affects the limbs, it can also manifest in other areas such as the head and neck regions. Regardless of its location, understanding the root cause, early recognition and intervention are key to managing this condition effectively.
Remember that recognizing the signs and symptoms is only the first step. Consulting a vein specialist, like Dr. Zmily, who specializes in lymphedema is crucial for accurate diagnosis and developing an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your unique needs.
Swelling
Swelling is a primary hallmark of lymphedema. It typically starts gradually and may worsen over time if left untreated. The affected area may feel heavy or uncomfortable due to the accumulation of excess fluid.
Those afflicted with lymphedema may wake up one morning and notice that their arm or leg feels unexpectedly heavy, almost as if it’s carrying extra weight. They might notice that their clothes fit differently or that their shoes suddenly seem tighter than usual. These could be subtle signs of lymphedema starting to manifest.
Changes in the Skin Color or Texture
Symptoms may include skin tightness, redness, or changes in skin texture. The skin in the affected area can become dry, rough, and prone to infections. In some cases, the swelling may lead to pain or discomfort.
Worsening Emotional Well Being
Worsening emotional well-being can also be a sign of this condition. Dealing with chronic swelling and associated physical limitations can take a toll on a person’s mental health, leading to feelings of frustration or reduced self-esteem.
Comparing Lymphedema With Other Conditions
When assessing and understanding lymphedema, it’s vital to distinguish it from other conditions that may present similar symptoms. While lymphedema is characterized by swelling of the extremities due to fluid retention in the lymph system, it can often be mistakenly confused with edema or vascular issues.
Edema refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling. It can occur as a result of various factors such as:
- Dehydration
- Prolonged sitting or standing
- Medication side effects
- Underlying health conditions like heart or kidney disease
Unlike lymphedema, which predominantly affects a specific area due to impaired lymphatic system function, edema is not confined to a particular region and can be generalized.
Vascular disorders like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) may also present with localized swelling, causing patients and professionals to confuse the condition for lymphedema. DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins of the body. If left untreated, the clot can travel through the bloodstream and pose a serious risk for complications. Unlike in lymphedema, where swelling is caused by impaired lymphatic drainage, DVT-related swelling is typically accompanied by pain and tenderness along the affected vein.
Consulting with a vein specialist like Dr. Zmily who specializes in both lymphedema and vascular disorders ensures an accurate diagnosis and tailored management approach based on individual needs.
Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnosing lymphedema requires a comprehensive evaluation that takes into account clinical presentation, patient history, and diagnostic tests. Understanding the underlying cause of the symptoms helps healthcare professionals such as your Michigan vein specialist formulate an effective treatment plan.
Initial Consultation
During an initial consultation, your Michigan vein specialist will discuss your medical history and inquire about any previous injuries, surgeries, or underlying medical conditions that could contribute to lymphedema development. He’ll also assess your symptoms such as limb swelling, skin discoloration, and any associated discomfort.
Vascular Ultrasound Studies
Vascular ultrasound studies play a crucial role in diagnosing lymphedema by providing detailed images of the lymphatic system and blood vessels. This non-invasive, non-radioactive imaging technique allows us to assess the flow of blood and lymph fluid, identify any blockages or abnormalities, and determine the extent of lymphatic damage.
During the ultrasound examination, high-frequency sound waves are used to create real-time images, helping to differentiate between lymphedema and other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment Options
Venous Ablation Therapy
In some cases, chronic venous insufficiency can contribute to or exacerbate lymphedema by putting additional pressure on the lymphatic system. Treating venous insufficiency through procedures like endovenous ablation can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of further complications related to both venous and lymphatic conditions.
Sclerotherapy
In cases where lymphedema is associated with or aggravated by concurrent venous insufficiency or varicose veins, treating the venous component with procedures like sclerotherapy may help alleviate some symptoms. By improving venous blood flow and reducing venous congestion, sclerotherapy can indirectly contribute to better lymphatic function and help manage swelling in some cases.
Microphlebectomy
Individuals with lymphedema may also have concurrent venous insufficiency or varicose veins. In these situations, addressing the venous component with procedures like microphlebectomy can help improve blood flow, reduce venous congestion, and contribute to better lymphatic function.
Managing Lymphedema With Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is an integral part of lymphedema management and can greatly contribute to reducing swelling, improving mobility, and enhancing overall function. Think of physical therapy for lymphedema as a personalized fitness program designed to restore strength and flexibility while considering the specific limitations and needs of individuals with limited lymphatic function.
Dr. Zmily can refer you to a physical therapist who can improve the effectiveness of your overall treatment.
Benefits of Physical Therapy for Lymphedema Management
- Personalized Exercise Plans: A physical therapist can develop an exercise routine that combines aerobic activities like walking or swimming with targeted exercises aimed at improving muscle strength and flexibility in the affected limb. These exercises help stimulate lymphatic flow, reduce fluid buildup, and enhance overall circulation.
- Personalized Skin-Care and Hygiene Advice: Physical therapists can provide education on self-care techniques, such as skincare and proper hygiene practices, which are crucial for preventing infections and maintaining optimal skin health in individuals with lymphedema.
- Guided Lifestyle Modifications: They may also offer guidance on lifestyle modifications that can help minimize the risk of exacerbating symptoms, such as avoiding extreme temperatures, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and practicing good posture.
- Patient Education: One of the key benefits of physical therapy in managing lymphedema is its focus on empowering patients through education and teaching them self-management techniques. By involving patients in their own care, they gain a sense of control over their condition, fostering independence in symptom management.
Why Choose Suburban Vein Center?
As a leading vein clinic in Michigan, we offer a variety of effective treatment options for lymphedema. These include:
- Manual lymphatic drainage
- Compression therapy
- Exercise
- Movement recommendations
- Lifestyle modifications to manage swelling
Our experienced vein specialist will work closely with you to develop an individualized treatment plan to address your specific needs and concerns. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and start your journey toward improved health and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lymphedema-related swelling tends to be more persistent, often affecting one limb more than the other, and can be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected area. On the other hand, venous insufficiency swelling may be more pronounced after prolonged sitting or standing and can be relieved by elevating the legs.
Yes, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing both lymphedema and venous insufficiency. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular low-impact exercises, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing, and elevating the legs when resting can all be beneficial. For individuals with lymphedema, practicing good skin care and avoiding injuries to the affected limb are also essential components of self-care.
While lymphedema can’t be completely cured, early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. With appropriate treatment, such as compression therapy, exercise, and self-care measures, individuals can experience reduced swelling, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life.
Yes, certain exercises can aid in managing lymphedema by promoting lymphatic flow and muscle pumping. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are generally recommended. Specialized exercises, called lymphedema exercises or Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT), may also be prescribed by a qualified therapist to target specific affected areas.
Call Suburban Vein Center and Take Control of Your Vascular Health Today!
Take the first step towards improved vascular health and enhanced quality of life by scheduling a consultation with Michigan’s leading vein specialist, Dr. Hamman Zmily, at Suburban Vein Center. Call our main office at (248) 480-0368 or fill out the contact form below and one of our friendly team members will get back to you shortly. Start your journey towards better vascular health at Suburban Vein Center’s Troy, Detroit, Rochester, or Taylor offices.